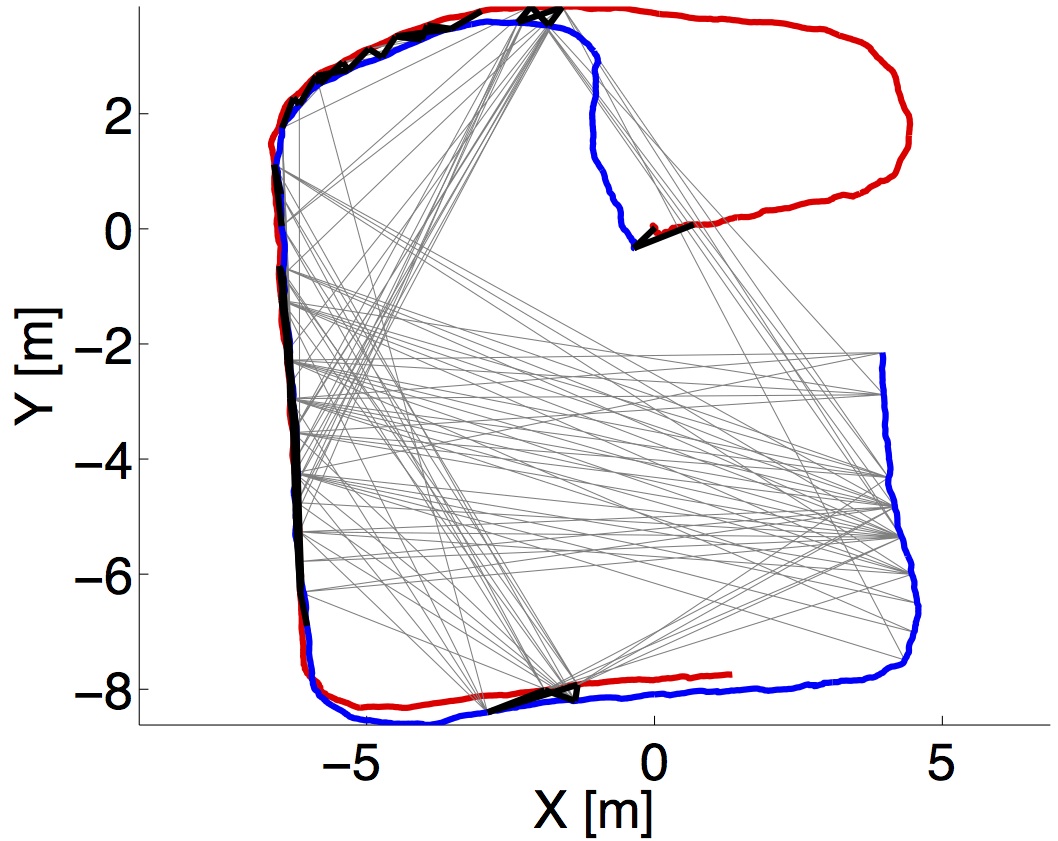
Below is a demonstration of our approach using a real-world experiment involving two quadrotors operating in indoor environment and sharing informative laser scans. As the robots do not have a common reference frame established, their initial poses are set to arbitrary values. Multi-robot candidate correspondences are generated by ICP-matching the shared laser scans. After some time, our approach successfully estimates the initial relative pose between the robots and determines multi-robot data association. From that moment, it becomes possible for the robots to robustly infer variables of interest, in this case each other’s trajectories, and to identify the inlier correspondences in newly arriving data.
Related Publications:
Journal Articles
- V. Indelman, E. Nelson, J. Dong, N. Michael, and F. Dellaert, “Incremental Distributed Inference from Arbitrary Poses and Unknown Data Association: Using Collaborating Robots to Establish a Common Reference,” IEEE Control Systems Magazine (CSM), Special Issue on Distributed Control and Estimation for Robotic Vehicle Networks, no. 2, 2016.
Book Chapters
- E. Nelson, V. Indelman, N. Michael, and F. Dellaert, “An Experimental Study of Robust Distributed Multi-Robot Data Association from Arbitrary Poses,” in Experimental Robotics, The 14th International Symposium on Experimental Robotics, Springer, 2016, pp. 323–338.
Conference Articles
- S. Pathak, A. Thomas, A. Feniger, and V. Indelman, “Towards Data Association Aware Belief Space Planning for Robust Active Perception,” in AI for Long-term Autonomy, workshop in conjunction with IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), May 2016.
- J. Dong, E. Nelson, V. Indelman, N. Michael, and F. Dellaert, “Distributed Real-time Cooperative Localization and Mapping using an Uncertainty-Aware Expectation Maximization Approach,” in IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), May 2015.
- V. Indelman, E. Nelson, N. Michael, and F. Dellaert, “Distributed Navigation with Unknown Initial Poses and Data Association via Expectation Maximization,” in 56th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Mar. 2015.
- V. Indelman, E. Nelson, N. Michael, and F. Dellaert, “Multi-Robot Pose Graph Localization and Data Association from Unknown Initial Relative Poses via Expectation Maximization,” in IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Jun. 2014.
- E. Nelson, V. Indelman, N. Michael, and F. Dellaert, “An Experimental Study of Robust Distributed Multi-Robot Data Association from Arbitrary Poses,” in International Symposium on Experimental Robotics (ISER), Jun. 2014.
- V. Indelman, N. Michael, and F. Dellaert, “Incremental Distributed Robust Inference from Arbitrary Robot Poses via EM and Model Selection,” in RSS Workshop on Distributed Control and Estimation for Robotic Vehicle Networks, Jul. 2014.